Intigriti Monthly Challenge 0125 by Godson
Challenge 0125 by Godson
Description
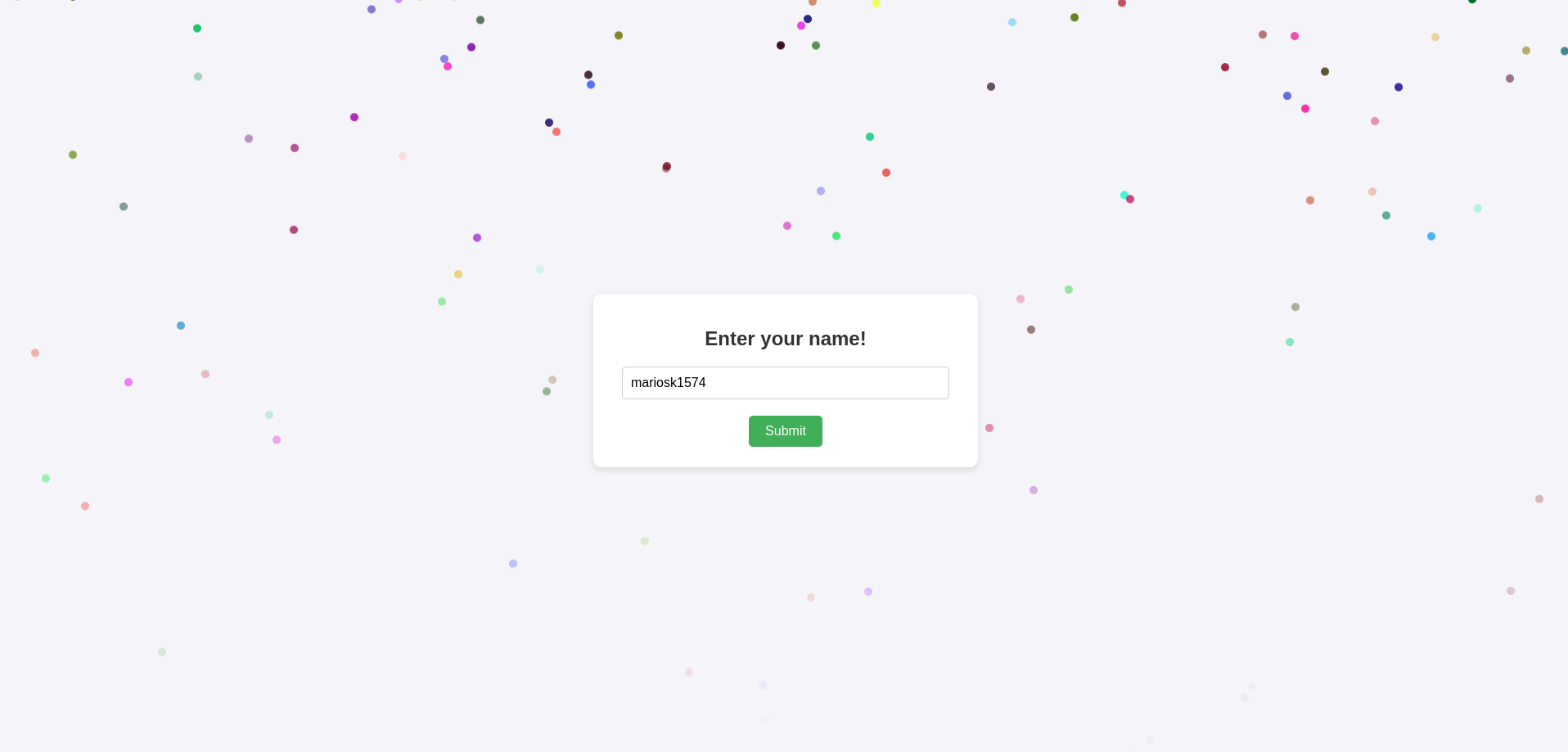
This challenge is part of Intigriti’s monthly challenges. The point of the challenge is to trigger XSS on the given domain with no user interaction required, and the solution must work on the latest version of both Chrome and Firefox.
https://challenge-0125.intigriti.io/challenge
Solution
First Look
The application takes user input via a form and reflects it in a modal after URL redirection.
Custom XSS sanitization functions
By taking a look at the HTML source code we find the following custom JS functions that are used to sanitize our input.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
function XSS() {
return decodeURIComponent(window.location.search).includes('<') || decodeURIComponent(window.location.search).includes('>') || decodeURIComponent(window.location.hash).includes('<') || decodeURIComponent(window.location.hash).includes('>')
}
function getParameterByName(name) {
var url = window.location.href;
name = name.replace(/[\[\]]/g, "\\$&");
var regex = new RegExp("[?&]" + name + "(=([^&#]*)|&|#|$)");
results = regex.exec(url);
if (!results) return null;
if (!results[2]) return '';
return decodeURIComponent(results[2].replace(/\+/g, " "));
}
// Function to redirect on form submit
function redirectToText(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const inputBox = document.getElementById('inputBox');
const text = encodeURIComponent(inputBox.value);
window.location.href = `/challenge?text=${text}`;
}
// Function to display modal if 'text' query param exists
function checkQueryParam() {
const text = getParameterByName('text');
if (text && XSS() === false) {
const modal = document.getElementById('modal');
const modalText = document.getElementById('modalText');
modalText.innerHTML = `Welcome, ${text}!`;
textForm.remove()
modal.style.display = 'flex';
}
}
// Function to close the modal
function closeModal() {
location.replace('/challenge')
}
// Function to generate random color
function getRandomColor() {
const letters = '0123456789ABCDEF';
let color = '#';
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
color += letters[Math.floor(Math.random() * 16)];
}
return color;
}
// Function to generate falling particles
function generateFallingParticles() {
const particlesContainer = document.getElementById("particles");
// Generate 100 particles with different animations, positions, and colors
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
let particle = document.createElement("div");
particle.classList.add("falling-particle");
// Randomize the particle's left position
particle.style.left = Math.random() * 100 + "vw"; // Left position from 0 to 100% of viewport width
// Randomize the particle's color
particle.style.backgroundColor = getRandomColor();
// Randomize animation delays
particle.style.animationDelay = Math.random() * 5 + "s"; // Random delay for staggered fall
particlesContainer.appendChild(particle);
}
}
// Generate particles when the page loads
window.onload = function () {
generateFallingParticles();
checkQueryParam();
};
XSS() Function
Checks whether there is a ‘<’ or ‘>’ symbol in the search part of the URL or in the fragment part of the URL, if at least one of these characters is included then the function returns true, otherswise it returns false.
Calling the XSS() function for the following URLs would return:
- https://challenge-0125.intigriti.io/challenge?text=mariosk1574 => false
- https://challenge-0125.intigriti.io/challenge?text=%3Cu%3E => true
- https://challenge-0125.intigriti.io/challenge?text=mariosk1574#test => false
- https://challenge-0125.intigriti.io/challenge?text=mariosk1574#%3Cu%3E => true
getParameterByName() Function
Extracts a query parameter’s value from the current URL.
- Get URL:
window.location.href - Escape Special Chars: Handles
[and]in the parameter name. - Regex Match: Finds the parameter and its value in the URL.
- Handle Results:
- Returns
nullif the parameter doesn’t exist. - Returns
''if the parameter has no value.
- Returns
- Decode Value: Converts URL-encoded chars (e.g.,
%20→ space,+→ space).
Example:
- URL: https://challenge-0125.intigriti.io/challenge?text=mariosk1574&age=
getParameterByName('text')→'mariosk1574'getParameterByName('age')→''getParameterByName('invalid')→null
Notes:
- Keep in mind that the function uses
window.location.hrefinstead ofwindow.location.search.
checkQueryParam() Function
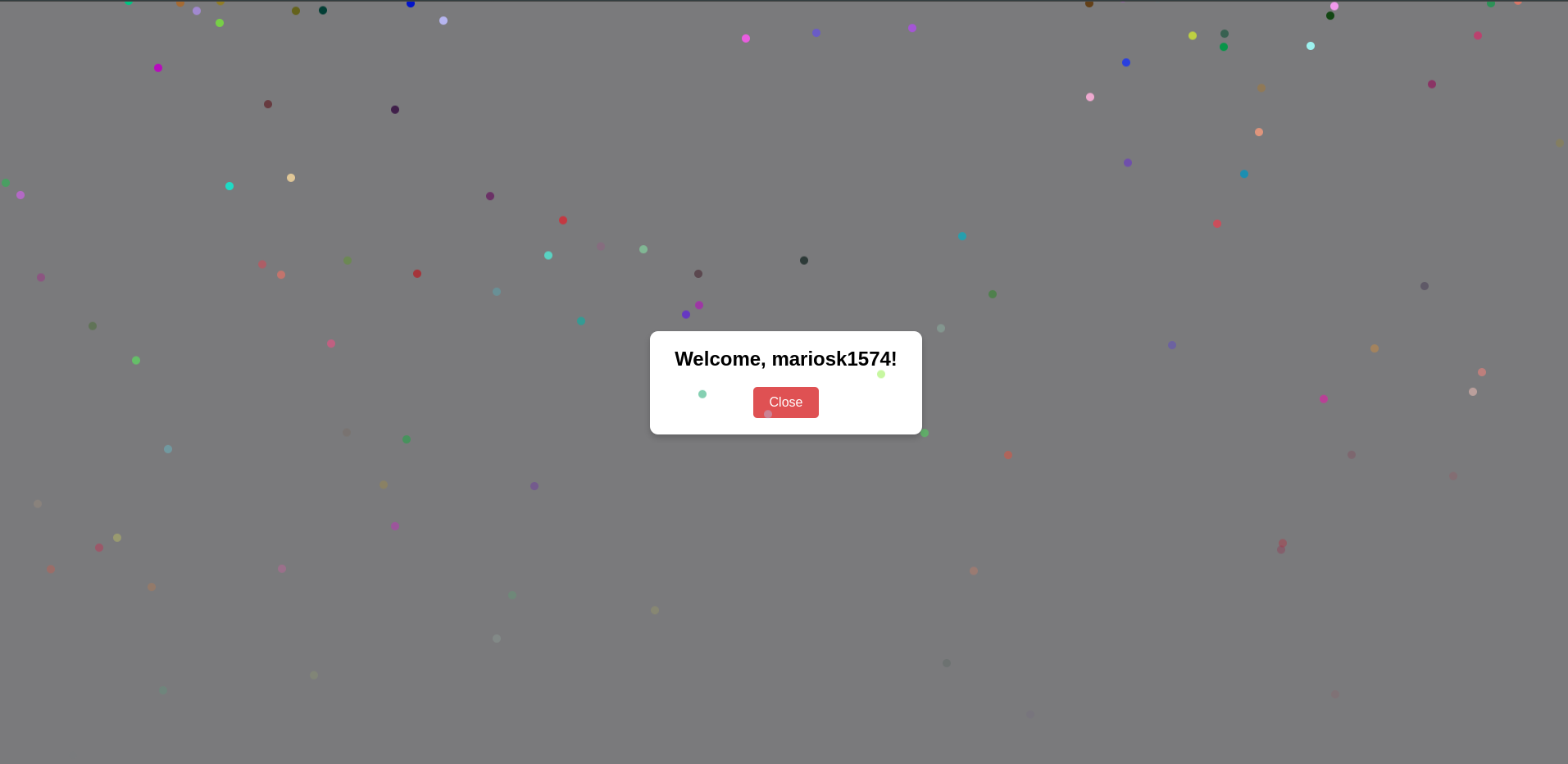
Checks for a text query parameter and displays a modal if valid.
- Get
textParameter: UsesgetParameterByName('text')to extract the value. - Validation:
- Checks if
textexists andXSS()returnsfalse.
- Checks if
- Display Modal:
- Updates the modal’s content with
Welcome, ${text}!.
- Updates the modal’s content with
window.onload Function
Runs when the page finishes loading.
- Generate Falling Particles: Calls
generateFallingParticles(). - Check Query Parameter: Calls
checkQueryParam()to handle thetextquery parameter and display a modal if valid.
The Path
So far we know the following:
- We provide our input via the text URL param.
- XSS() checks if there are any illegal characters in our input but only takes into account
window.location.searchpart. - getParameterByName() extracts the value from text param but takes into account the whole URL
window.location.href.
Do you see the problem?
There is a discrepancy between points 2 and 3. What will happen if we provide our input as part of the path?
URL Normalization and Payload Explanation
URL Normalization
URL normalization is the process of transforming a URL into a standardized format. This includes:
- Removing redundant path segments: For example,
/challenge/../becomes/. - Decoding percent-encoded characters: For example,
%2fbecomes/. - Resolving relative paths: For example,
/challenge/foo/../barbecomes/challenge/bar.
In this challenge, the URL normalization process plays a key role in how the text parameter is interpreted and displayed.
Payload Breakdown
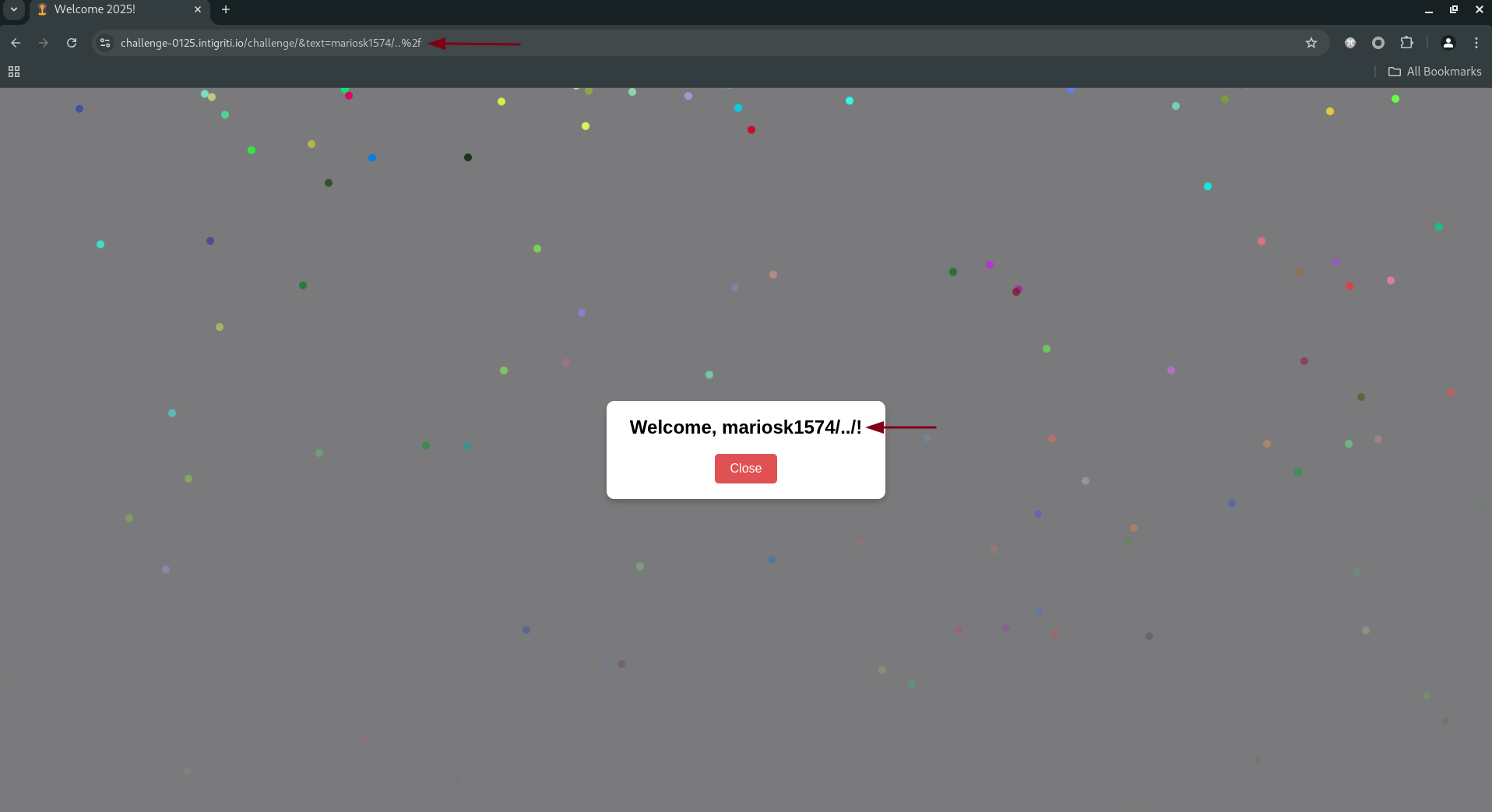
The payload: https://challenge-0125.intigriti.io/challenge/&text=mariosk1574/..%2f
- URL Structure:
- The URL contains a
textparameter with the valuemariosk1574/..%2f. - The
%2fis the URL-encoded representation of/.
- The URL contains a
- Normalization Process:
- When the browser processes the URL, it normalizes the path:
challenge/&text=mariosk1574/..%2fbecomeschallenge/&text=mariosk1574/../.
- The
../is interpreted as a relative path, moving up one directory level.
- When the browser processes the URL, it normalizes the path:
- Resulting Path:
- After normalization, the
textparameter effectively becomesmariosk1574/../. - This is passed to the
getParameterByNamefunction, which extracts the valuemariosk1574/../.
- After normalization, the
- Modal Display:
- The
checkQueryParamfunction sets the modal’s innerHTML to:1
modalText.innerHTML = `Welcome, ${text}!`;
- Since
textismariosk1574/../, the modal displays:1
Welcome, mariosk1574/../!
- The
Why This Works
- URL Encoding: The
%2fencoding allows the/character to be included in thetextparameter without breaking the URL structure. - Path Traversal: The
../sequence is normalized by the browser, but it doesn’t affect the server-side logic because thetextparameter is processed client-side. - Client-Side Rendering: The
innerHTMLassignment in the modal directly uses the normalized value, allowing the payload to be displayed as-is.
Exploitation
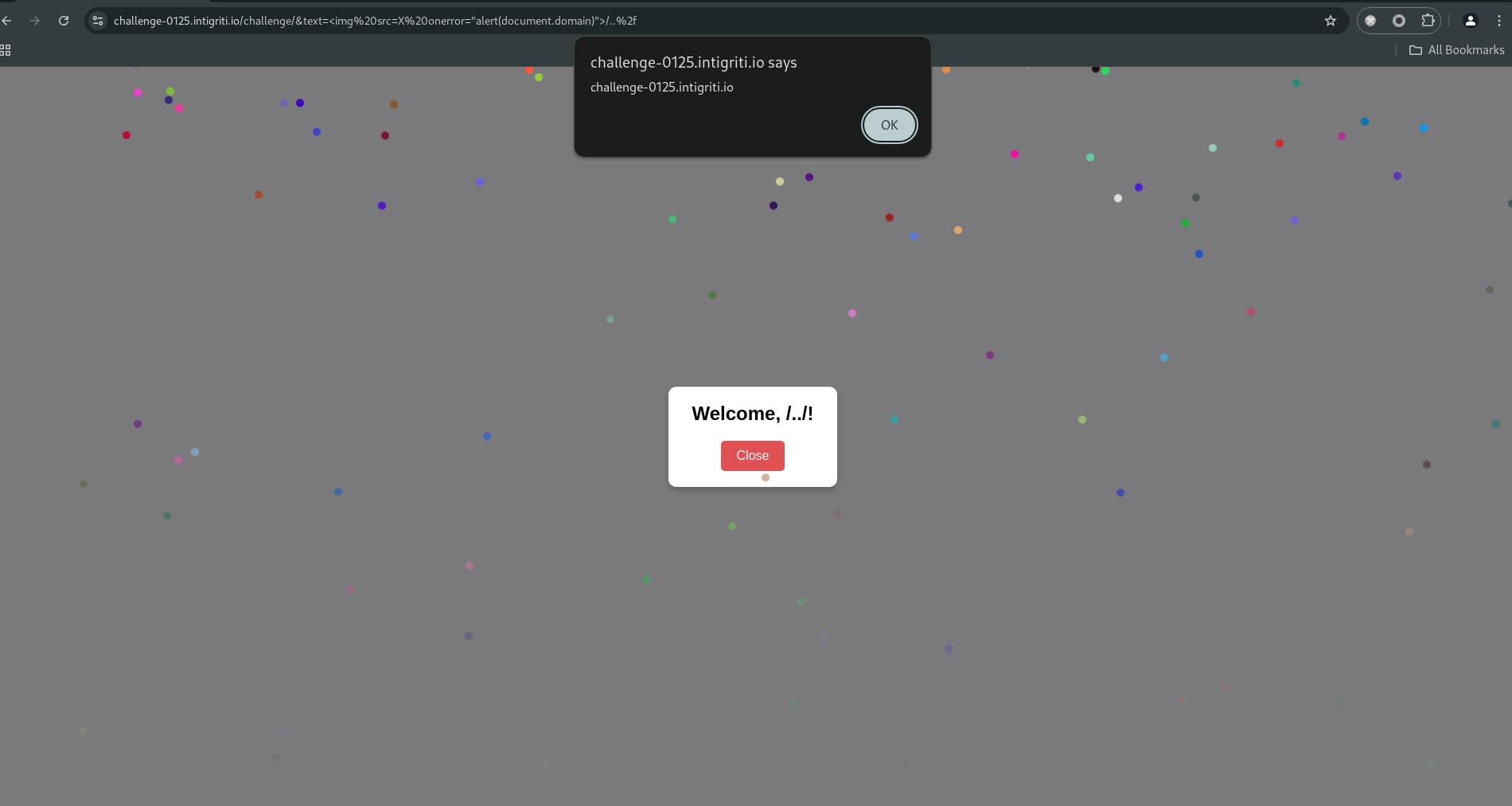
Our goal is to inject a payload that bypasses the XSS() check and executes JavaScript in the context of the modal. Since the innerHTML assignment in the modal does not allow <script> tags, we use an <img> tag with a broken src to trigger the onerror event.
Final Payload:
1
<img src=X onerror="alert(document.domain)">